EEG (ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM)
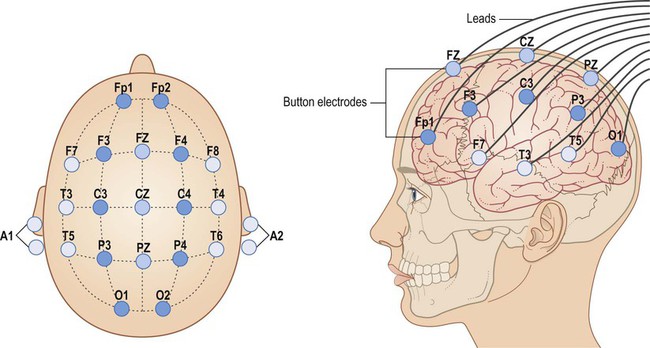
An EEG (electroencephalogram) is a test that detects electrical activity of brain using small, metal discs (electrodes) attached to the scalp. The brain cells communicate via electrical impulses and are active all the time, even during sleep. This activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording.
German physiologist and psychiatrist Hans Berger (1873–1941) recorded the first human EEG in 1924. Expanding on work previously conducted on animals by Richard Caton and others, Berger also invented the electroencephalogram (giving the device its name), an invention described "as one of the most surprising, remarkable, and momentous developments in the history of clinical neurology”
The first human EEG recording obtained by Hans Berger in 1924. The upper tracing is EEG, and the lower is a 10 Hz timing signal.
Uses of EEG :
An EEG is used to detect problems in the electrical activity of the brain that may be associated with certain brain disorders. The measurements given by an EEG are used to confirm or rule out various conditions, including :
- Seizure disorders (such as epilepsy)
- Encephalitis (an inflammation of the brain)
- Brain tumor
- Encephalopathy (Brain dysfunction due to metabolic disturbances, medication etc.)
- Memory problems and Dementia
- Sleep disorders
When someone is in a coma, an EEG may be performed to determine the level of brain activity.
Are There Risks Associated with an EEG ?
There are no risks associated with an EEG. The test is painless and safe.
Patient with epilepsy or another seizure disorder, the stimuli presented during the test (such as a flashing light or hyperventilation) may cause a seizure. However, our technician performing the EEG is trained to safely manage the situation should this occur.
Is any Prepare require for an EEG?
Before the test, patient should take the following steps:
- Wash hair with shampoo before the EEG, keep hair dry and don’t put any products (such as oil, sprays or gels) in hair till the procedure is over.
- Make a list of medications with doses and give it to the technician performing the EEG.
- Avoid consuming caffeine containing food or drinks for at least eight hours prior to the test.
- In some cases sleep deprivation is required. In this situation it is better patient remains awake during the night before the test.
- In small number of cases specially children, mentally retarded etc. sedation is required during EEG.
After the EEG is over, patient can continue his or her regular activities. However, if sedative is given, effect of medication remains for a sometime. Patient need rest and until the medication effect worn off.
What Can I Expect During an EEG?
An EEG measures the electrical impulses in your brain by using several electrodes that are attached to your scalp. An electrode is a conductor through which an electric current enters or leaves. The electrodes transfer information from your brain to a machine that measures and records the data.
- Patient has to lie down on your back on a bed.
- The technician measure head and mark where the electrodes will be placed. These spots are then scrubbed with a special cream that helps the electrodes get a high-quality reading.
- The technician put a sticky gel adhesive on 32 electrodes. They will then be attached to various spots on your scalp.
- Once the test begins, the electrodes send electrical impulse data from your brain to the recording machine. This machine converts the electrical impulses into visual patterns that can be seen on a screen. These patterns are saved to a computer.
- The technician may instruct you to do certain things while the test is in progress. They may ask you to lie still, close your eyes, breathe deeply, or look at stimuli (such as a flashing light or a picture).
- After the test is complete, the technician will remove the electrodes from your scalp.
What Do the EEG Test Results Mean?
A neurologist (someone who specializes in nervous system disorders) interprets the recordings taken from the EEG and then sends the results to your doctor. Your doctor may schedule an appointment to go over the test results with you.
Normal Results
Electrical activity in the brain is seen in an EEG as a pattern of waves. Different levels of consciousness, such as sleeping and waking, have a specific range of frequencies of waves per second that are considered normal. For example, the wave patterns move faster when you’re awake than when you’re asleep. The EEG will show if the frequency of waves or patterns are normal. Normal activity typically means you don’t have a brain disorder.
Abnormal Results
Abnormal EEG results may be due to:
- epilepsy or another seizure disorder
- abnormal bleeding or hemorrhage
- sleep disorder
- encephalitis (swelling of the brain)
- a tumor
- dead tissue due to a blockage of blood flow
- migraines
- alcohol or drug abuse
- head injury
It’s very important to discuss your test results with your doctor. Before you review the results with them, it may be helpful to write down any questions you might want to ask. Be sure to speak up if there’s anything about your results that you don’t understand.